What is methanization? Understanding the process and its challenges
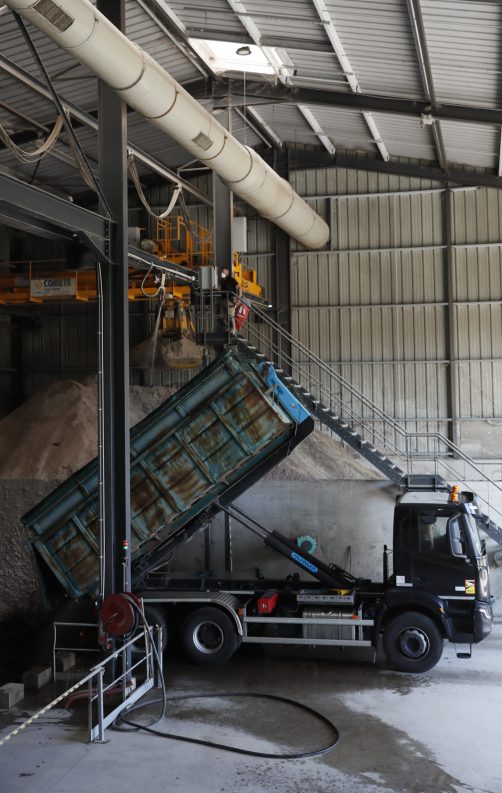
Feedstock for biomethane production
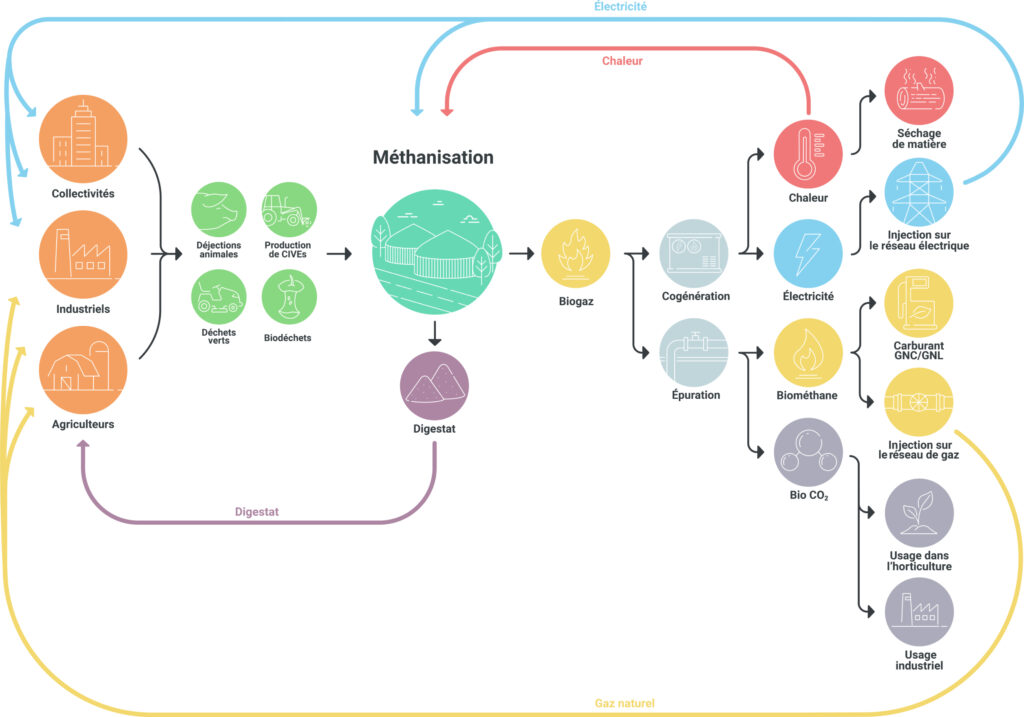
Any organic waste can be used as feedstock for the production of biogas or biomethane:

Agricultural waste
Dry or liquid manure from pigs and cattle, agricultural residues, poultry manure, etc.

Community waste
Biowaste from the catering industry, grass clippings, chaff, roadside mowing, silage. etc.

Food industry waste
Animal or vegetable fat, fruit, vegetables, etc.

Household waste
Kitchen waste, wastewater, garden waste, etc.
The digester
Once the organic waste is in the digester – which recreates the optimal conditions for digestion (a low-pressure, oxygen-free, watertight environment with a constant temperature of 38°C) – and thanks to the microorganisms and bacteria that break it down, the organic waste ferments to create biogas or biomethane when purified and then is injected into the GRDF system (France’s main distributor of natural gas).
There are two types of digesters: liquid and discontinuous dry digesters.
Biogas recovery
Biogas recovery is a determining factor in the financial success of any given biomethane production project. There are currently several ways to recover biogas. The injection of biomethane into natural gas networks and cogeneration (generation of electricity) are the two most common recovery methods used in France and around the world. The decomposition of organic matter also produces a humus-rich, partially stabilized residue called digestate, which can then be reused for agricultural purposes as a natural and organic fertiliser.
The benefits of biomethane production

For farmers
• New business opportunities
• A stable form of additional income over 15 years
• Agronomic improvement of outflows
• Reinforcement of the land-farming relationship
• Production of 100% natural fertiliser for spreading on fields

For local authorities
• Creation of local waste processing industry
• Increase in regional energy autonomy
• Potential new business opportunities (installation of a local heat distribution system)
• Fewer odour nuisances for locals and a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.

For manufacturers
• Capture of CH4 emissions
• Local generation and sale of electricity, heat and biomethane
• Reduction in need for waste transport.














